![]() This tutorial is part of our tutorial series on WordPress Security. In this tutorial, we review additional web browser security tips.
This tutorial is part of our tutorial series on WordPress Security. In this tutorial, we review additional web browser security tips.
***
Web Browser Security – Useful Tips
In the previous section of this tutorial, we covered a number of important areas related to browser security information. In this section, you will complete the tutorial on browser security by learning some additional tips on ways that your browser contributes to the overall security of your online assets.
Review & Disable Unnecessary Browser Features
Your web browser includes certain features that contribute to the browser’s operation and online security. Some of these features can be disabled. Before deciding whether or not to disable these features, however, it’s important to know what they do.
ActiveX
ActiveX is a software component or an add-on of the Windows operating systems and comes pre-installed on computers with the Internet Explorer browser. ActiveX is required by some websites to access certain elements or perform actions, and for improving general user browsing experience. When visiting certain websites, you may see a request to install ActiveX.
Malicious users may use ActiveX to create and add malicious ActiveX software to web pages in order to damage computers. If you don’t need ActiveX, don’t install it, especially if you don’t trust the publisher or the website.
Java
Java is a programming language developed to create applications on computers or active content on websites. Java has two components: the Java application that runs on our computers and the browser plug-in, which we recommend disabling unless you really need to use it.
The Java browser plug-in presents a number of security holes that allow hackers to access your personal data, such as credit card information or banking account credentials.
Javascript
JavaScript is a programming language designed to create interactive web pages and is used mostly for displaying dynamic content and improving users’ online experience. The problem with JavaScript is that many viruses are script-based and many scripts can be used to delete system files or perform other malicious tasks.
Cookies
Cookies are files which are stored on your browser and contain data about your browsing history. Cookies are commonly used in websites to reduce the burden on computer servers to store information about the sites that you are visiting. Websites use cookies to improve browsing session, but this behavior has also given rise to privacy concerns and security issues.
Extensions
Extensions are software add-ons that add or modify a feature or a functionality in web browsers. Some extensions allow you to block ads, watch videos or play games online, access information on other websites, integrate user experience with social media websites, improve your online session, etc. On the downside, extensions can also be used to inject ads into the sites you visit or track your browsing activity for malicious purposes. Do not install extensions from suspicious sites or publishers.
Block Data Tracking
Many websites use advertising network scripts to track what pages you visit online in order to serve you advertisements based on your specific interests. For example, you may have noticed in the past visiting a website for a specific product or information, and then visiting another website and seeing advertisements for the product you viewed earlier.
Some companies track the pages you visit and then compile the data to be analyzed or sold to advertisers, or track which pages you visit on their site and how long you spend on each page to try and determine what you are interested in.
Browsers give you the option to disable tracking, which then lets websites you visit know that you don’t want to be tracked …

![]()
Enabling “Do Not Track” doesn’t actually change any browser privacy settings. When “Do Not Track” is enabled, your web browser merely requests each website that you visit not to track you.
Websites have to be updated to take notice of your request, and most will simply ignore your request. Websites that take notice of your request may disable all tracking, or they may choose to disable targeted advertising and show you generic advertisements instead, or they may disable tracking by third-party website, and continue tracking you to collect data for their own purposes.
The bottom line: Just because you have disabled tracking on your browser, it doesn’t mean that the sites you visit will respect your request.
Private Browsing
Most web browsers provide an option to browse the web without having your history saved. This is useful if you use a shared computer and don’t want others to see which sites you are visiting.
![]()
Private Browsing doesn’t make you anonymous on the Internet. Your IP address leaves a “digital footprint” wherever you go online, and this can be tracked by your Internet service provider, employer, or the sites themselves.To surf the web anonymously, you will need to use anonymous proxy servers. As the subject of anonymous web surfing is beyond the scope of our tutorials, we have included a link to an article on “How to Surf the Web Anonymously” in the ‘References’ section at the end of this tutorial.
Private Browsing also doesn’t protect you from keyloggers or spyware that may be installed on your computer.
In Firefox, you can access private browsing to browse the Internet without saving any information about which sites and pages you’ve visited, either by selecting ‘New Private Window’ from the Firefox menu …
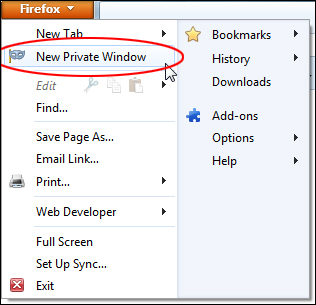
Or by right-clicking on a hyperlink when visiting pages on a website, and selecting ‘Open Link in New Private Window’ …

You can tell whether you are browsing normally or privately by looking at the topmost Firefox window tab icon …

Note: You can have both types of windows open and alternate your browsing activity by switching from one window to the other.
In Google Chrome, the private browsing mode is is called “incognito”.
You can access this feature by clicking on the ‘Control’ button and selecting ‘new incognito window’ …

A private browsing tab will open up, allowing you to view pages that won’t be recorded in your browser’s history after you’ve finished your browsing session and closed all of your ‘incognito’ tabs …

Note: Browsing in incognito mode only keeps Google Chrome from storing information about the websites you’ve visited. Your IP address can still be tracked and recorded by the websites you visit. Also, any files you download and save to your computer or mobile devices will be kept.
Here’s how incognito mode works:
- Webpages that you open and files that you download while you’re incognito aren’t recorded in your browsing and download histories.
- All new cookies are deleted after you close all incognito windows that you’ve opened.
- Changes you make to your Google Chrome bookmarks and general settings while in incognito mode are still saved.
- You can have both incognito mode windows and regular windows open at the same time, and switch between the two.
Refer to the browser support sites listed in the ‘Reference’ section at the end of this tutorial to learn more about private browsing.
Clearing Recent File Usage Records
Even if you delete records of your browsing activity, Windows may still keep a record of your most recently used files on your computer’s temporary file storage area. To delete these records, you will need to clean your registry.
To learn how to clean your registry, search online for tutorials on how to harden your computer security.

This is the end of this tutorial. Hopefully, this tutorial has provided you with useful information on ways to secure your web browser and how to safely browse the internet. To view previews sections of this tutorial, click on one of the links below:
- Web Browser Security Overview
- How To Configure Your Web Browser’s Security And Privacy Settings
- Important Web Browser Security Information
- Return To WordPress Security Tutorials
References
- Google Chrome: Incognito Mode – (Browse In Private)
- Firefox – Private Browsing
- How To Surf The Web Anonymously
- Why Enabling “Do Not Track” Doesn’t Stop You From Being Tracked
- Firefox Browser Support
- Google Chrome Browser Support
- Internet Explorer Browser Support
- Apple Browser Support
***
"Learning WordPress has been a huge stumbling block for me. I've been looking for something that covers absolutely everything but doesn't cost an arm and a leg. Thank you so much ... you have just provided me with what I have been looking for! Truly appreciated!" - Tanya
***

