![]() This tutorial is part of our tutorial series on WordPress Security. In this tutorial, you will learn how to configure your web browser’s security and privacy settings.
This tutorial is part of our tutorial series on WordPress Security. In this tutorial, you will learn how to configure your web browser’s security and privacy settings.
***
How To Configure Web Browser Security Settings
Regardless of the browser you are using, there are security settings that you need to know about in order to have greater control over your web browsing privacy and security.
In this section we look at how to configure privacy and security settings for:
- Browser Cookies
- Browser History
- Browser Cache
Browser Cookies
The main purpose of cookies is to identify users and possibly prepare customized Web pages for them. When you enter a Web site using cookies, you may be asked to fill out a form providing such information as your name and interests.
This information is packaged into a cookie and sent to your Web browser which stores it for later use. The next time you go to the same Web site, your browser will send the cookie to the Web server.
The server can use this information to present you with custom Web pages. So, for example, instead of seeing just a generic welcome page you might see a welcome page with your name on it.
(Source: Webopedia)
Most sites that provide some form of e-commerce, membership or subscriptions use cookies.
For example, if you shop at Amazon or have an account with eBay, your login details and preferences will be stored in a cookie in your browser. This allows the sites to remember your settings and previous activities on the site …

It also allows the sites to retrieve the information stored in the cookie when you return to provide you with a personalized user experience …

Your WordPress login is also stored in a browser cookie, as are the logins of any sites you visit, especially if you tick the ‘remember me’ box commonly found in many login forms …

Most users have no idea that cookies are being stored in their computer, or how long the cookies in their browser are storing the information for. Some websites may also place more than one cookie in your browser.
Cookies help to personalize your experience when you visit websites, but they also have disadvantages and can present security risks.
For instance, cookies can identify your IP address and give the sites you visit information about your purchasing behavior that could be onsold to advertisers. This could leave you open to exploitation not only by marketing companies, but other third-party agents that you may not even know about …

In terms of security, cookies log the sites you visit, which can create privacy issues and provide useful information for anyone trying to build a profile of your online behavior …

Configuring Your Browser Cookie Settings
Information about your browser cookies is stored in your browser’s ‘Options’ or ‘Settings’ section, depending on the browser you are using.
For example, in Firefox, you can access information about your cookies by selecting the ‘Options’ menu …

In the ‘Option’ > ‘Privacy’ tab, select ‘Use custom settings for history’ from the drop-down menu in the ‘History’ section …

This will display a number of additional settings that will allow you to configure things such as:
- Whether to accept cookies from sites or not
- How to handle third-party cookies (always accept, accept cookies from visited sites only, or never accept cookies)
- How long to keep cookies on your browser for (keep cookies until they expire, keep cookies until you close Firefox and end your browser session, or let Firefox ask you every time)
- Create exception rules for handling cookies from specific sites (e.g. block cookies just from some sections of a website but not other areas)
- View stored cookies
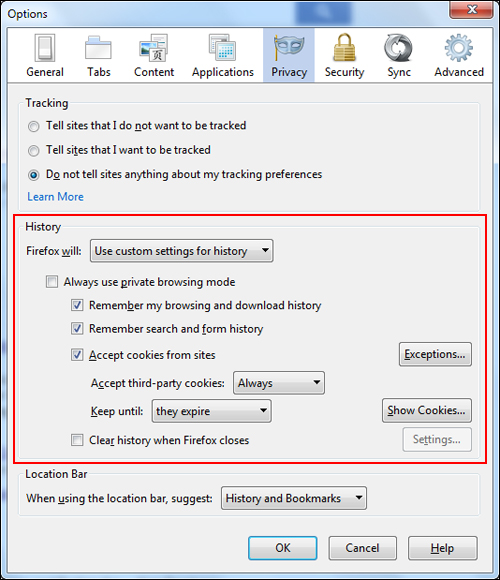
Click on the ‘Ok’ button when finished to update your settings.
In Google Chrome, you can access your cookie settings information by clicking on the Google Chrome control button and selecting ‘Settings’ from the menu …

Click on ‘Show advanced settings’ …

In the ‘Settings’ > ‘Privacy’ section, click on the ‘Content settings…’ button …

This brings up the ‘Content settings’ window. Configure your cookie settings in the ‘Cookies’ section of the screen …

To prevent any cookies from being placed on your computer, select “Block third-party cookies and site data” …

Click ‘Done’ when finished to update your settings.
To configure your cookies in Internet Explorer, click on the ‘Tools’ button and select ‘Internet options’ …

Change your cookie settings in the ‘Internet Options’ > ‘Privacy’ tab …

To configure your cookies in Safari, select the ‘Safari’ > ‘Preferences’ menu option …

And click on the ‘Security’ tab …

To learn more about configuring cookie settings in the above browsers, visit the help pages below:
- How To Enable And Disable Cookies In Firefox
- Manage Your Google Chrome Cookies And Site Data
- Block Or Allow Cookies In Windows Internet Explorer
- Safari – Managing Information Stored By Websites
How To Delete Browser Cookies
You may want to delete some or all of the cookies stored in your browser for privacy reasons, to improve the performance of your browser, or to remove an unwanted event, activity or error that has been caused by a cookie (e.g. your browser keeps redirecting to an advertisement, to an expired login page, or to a site containing information placed by a previous cookie).
In Firefox, you can remove cookies as follows:
In the ‘Options’ > ‘Privacy’ tab, click on ‘remove individual cookies’ …

This brings up the ‘Cookies’ window, listing all of the cookies that are stored on your browser …

You can delete an individual cookie by selecting it from the list and clicking the ‘Remove Cookies’ button …

Or click on the ‘Remove All Cookies’ button to clear all cookies from your browser …

All cookies that were stored in your browser will be deleted …

Note: After clearing all cookies from your browser, you will probably notice that some of your most visited sites no longer remember who you are or your preferences, and you may have to login again to access any sites that you were logged into previously.
In Google Chrome, navigate to the ‘Content settings’ > ‘Cookies’ section, and click on ‘All cookies and site data…’

You will be able to see all the cookies that are currently stored in your browser …

You can click on cookies to delete them individually, or click on the ‘Remove all’ button to clear all cookies on your browser …

Remember to click ‘Done’ when finished.
To learn how to delete cookies in Internet Explorer and Safari browsers, visit the help pages below:
Browser History
Your browser also keeps track of all the sites you have visited over a period of time. This allows anyone with access to your computer to see which sites you have visited …

You can access your browser history in Firefox by going to ‘History’ > ‘Show All History’ …

To view your browser history in Google Chrome, click on the control button and select ‘History’ from the menu …

Accessing your browser history on Internet Explorer and Safari is also simple. Search online for “view history in browser name” if you need help with this.
Configuring Browser History Settings
To configure your browser history settings in Firefox, go to the ‘ Options’ > ‘Privacy’ tab and select an option from the dropdown menu in the ‘History’ section …

You can allow Firefox to remember your browsing history, to never remember it, or you can configure custom settings for your browser history (.e.g. have Firefox delete your history when you quit the browser) …

Refer to the earlier documentation in this tutorial and help pages in the ‘Reference’ section to learn more about managing browser history in your particular web browser.
Deleting Browser History
To delete the history in Firefox, go to ‘Options’ > ‘Privacy’ and click on ‘clear your recent history’ …

You can select various browser data (see next section below) and time ranges to clear; from the last hour of browsing online, to deleting everything, by selecting your options and clicking on the ‘Clear Now’ button …

You can allow Firefox to remember your browsing history, to never remember it, or you can configure custom settings for your browser history (.e.g. have Firefox delete your history when you quit the browser) …

Refer to the earlier documentation in this tutorial and help pages in the ‘Reference’ section to learn more about managing browser history in your particular web browser.
Browser Cache
As well as the security benefits, clearing your browser cache can fix many browser problems, such as browser plugin crashes, stored cache content conflicting with live content, and the browser preventing you from seeing updated content.
Clearing Your Cache
To clear your cache in Firefox, go to ‘Options’ > ‘Privacy’ and click on ‘clear your recent history’ …

Select ‘Everything’ in ‘Time range to clear:’ and make sure that ‘Cache’ is selected, then click on the ‘Clear Now’ button …

Note: To only clear the cache, make sure that no other options but ‘cache’ are selected before clicking on the ‘Clear Now’ button …
In Google Chrome, click the ‘Clear browsing data…’ button …

Select the items you want to delete and the time frame, then click on ‘Clear browsing data’ …

In Internet Explorer, your browser cache settings can be accessed by clicking on the ‘Tools’ button and selecting ‘Internet Options’ …

Select the ‘Internet Options’ > ‘General’ tab and configure your options in the ‘Browsing history’ section …

To empty your cache in Safari, go to ‘Safari’ > ‘Empty Cache’ …

You will be asked to confirm your decision to empty the cache. Click on ‘Empty’ to proceed and delete the content of your cache …

![]() Refer to the browser support sites listed in the ‘Reference’ section to learn more about managing your web browser’s cache.
Refer to the browser support sites listed in the ‘Reference’ section to learn more about managing your web browser’s cache.

This is the end of this section. In the next section, we review important web browser security information. To continue, click on the link below:
See also …
References
- What Are Browser Cookies
- How To Block Or Allow Cookies In Windows Browsers
- Manage Your Cookies And Site Data
- What Is Browser Cache
- How To Clear Browser Cache And Cookies
- How To Clear Firefox Cache
- Empty Cache In Apple Safari Browser
- Firefox Browser Support
- Google Chrome Browser Support
- Internet Explorer Browser Support
- Apple Browser Support
***
"If you're new to WordPress, this can stand on its own as a training course and will stay with you as you progress from beginner to advanced and even guru status." - Bruce (Columbus, Ohio)
***