
Wouldn’t it be great if after adding a new post to your site, the following could take place … all from your page address:
- Users could easily determine what your content was about,
- Search engines could find your posts faster,
- Each content item you create on your website or blog would have its own unique ID, making your content easier to manage.
Well, with WordPress permalinks you can!
How To Set Up And Use WordPress Permalinks
What Is A Permalink?
A permalink is the permanent URL to an individual WordPress post, category, or other taxonomy (a way to group things together) like archives.
A permalink is the URL that visitors and search engines will use to link to your articles or sections of your site or the links you send in an email pointing to posts on your site. Some people also call permalinks “pretty” URLs.
Permalinks make the web address pointing to each post on your website permanent, hence a perma-link.
Why Do You Need To Use Permalinks?
As you have probably heard by now, WordPress is one of the best CMS tools you can use when it comes to SEO.
WordPress is not only well optimized straight out of the box, but there are excellent SEO plugins you can use that will help to fine tuned its SEO aspect.
If you are looking to optimize the SEO aspect of your site or blog, then you should not ignore the importance of its URLs. Search engines like Google place considerable weight on the URL structure of a site.
Permalinks are used to make the links on your site into “prettier” and more “search engine friendly” URLs. Permalinks can also improve the usability, aesthetics, and forward-compatibility of your links.
Now … let’s take a look at why you may need to configure your permalinks if publishing content in WordPress.
By default, a WordPress installation uses a non-search engine friendly link-naming structure for your posts that looks like this …
 The link structure shown above is used by WordPress to find information inside its database. It doesn’t really mean anything to search engines or visitors, and it doesn’t help your website with on-site SEO.
The link structure shown above is used by WordPress to find information inside its database. It doesn’t really mean anything to search engines or visitors, and it doesn’t help your website with on-site SEO.
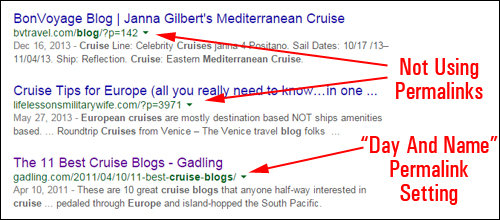
As the screenshot below shows, many WordPress site owners have not yet configured their permalinks …
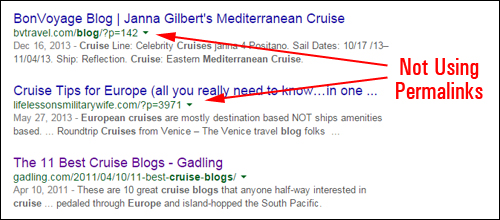
Although Google is still indexing the above sites, many site owners are missing out on extra SEO benefits.
To get maximum SEO benefit out of using WordPress and improve your site’s traffic results, you should set up your permalinks structure to make it more SEO-friendly by displaying relevant keywords in your URL, instead of meaningless numbers and symbols.
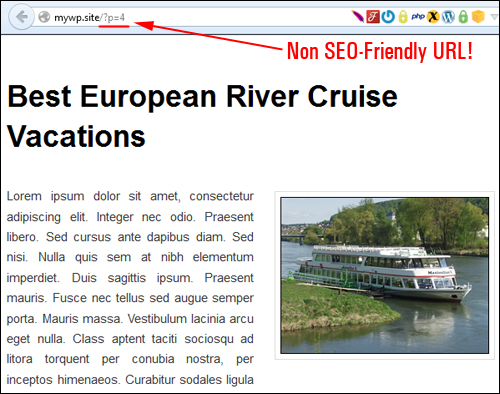
WordPress lets you create a custom URL structure for your published posts, so your content can go from something that is non-SEO friendly like this …
To something like this …
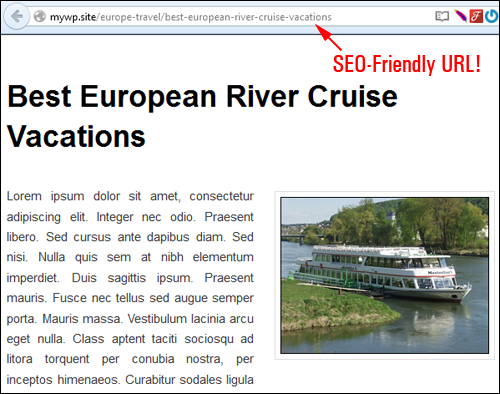
In this step-by-step tutorial, you will learn how to set up your WordPress permalinks to display your posts using SEO-friendly URLs instead of the out-of-the-box URL structure and help every new post you add automatically get better indexing in search engines like Google.
Changing Your WordPress Permalinks
In your WordPress dashboard section select, Settings > Permalinks …
This brings you to the Permalink Settings screen …
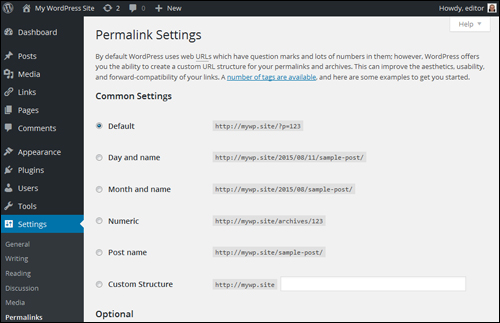
As mentioned earlier, by default WordPress web URLs use characters like question marks and numbers to create unique Post Ids and URLs. We want to create a “pretty” permalink instead for our posts. To do this, we will need to specify a different Permalink structure than the default one.
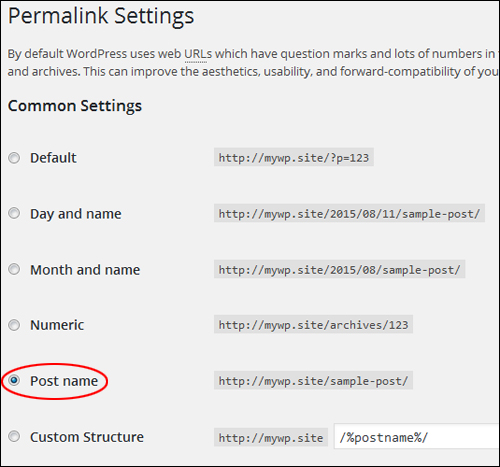
Common Permalink Settings
In the Common Settings section, select Custom Structure, then add one or more ‘tags’ (see below) to create search engine-friendly URLs …
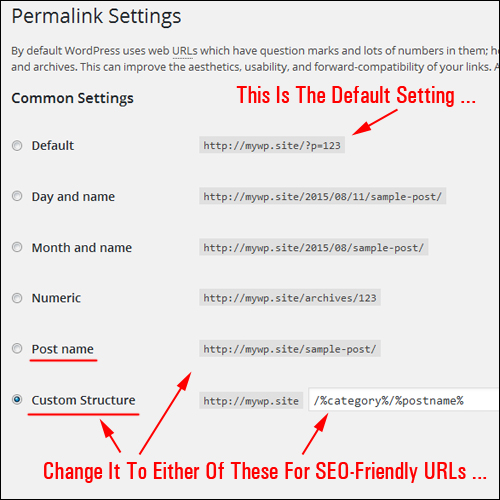
(Change your permalink settings to create search engine-friendly URLs)
If you use the custom permalink structure shown in the example above, your URL would look something like this:
http://www.mytravelsite.com/travel-tips/river-cruise-holiday-bargains
Instead of this …
http://www.mytravelsite.com/?p=19
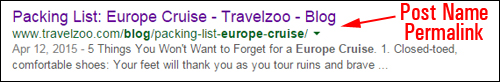
(Using permalinks helps visitors and search engines understand what the post is about)
Creating SEO-Friendly Tags
“Pretty” URLs, or SEO-friendly URLs, are created by adding one or more ‘tags’ in the Custom Structure field:
- %year% – The year the post gets published, displayed as four digits (e.g. ‘2013’)
- %monthnum% – The month the post gets published (e.g. ‘05’)
- %day% – The day your post is published (e.g. ‘10’)
- %hour% – The hour your post is published (e.g. ‘03’)
- %minute% – Minute of the hour (e.g. ‘31’)
- %second% – Second of the minute (e.g. ‘41’)
- %post_id% – The unique ID # of the post (e.g. ‘1983’)
- %postname% – A sanitized version of the post title. For example, if your post title is ”It Ain’t Worth Doin’ No More!”, the postname tag will convert this into “it-aint-worth-doin-no-more” (all characters converted to lower case and no punctuation symbols) in the URL. Tip: You can always edit the words in your post titles in the post slug field on the Add/Edit Post/Page screens.
- %category% – A sanitized version of the category name. Nested sub-categories appear as nested directories in the URI (Uniform Resource Identifier – the string of characters used in the URL). Tip: You can edit this text in the category slug field in the New/Edit Category screens.
- %author% – A correctly formatted version of the author name.
Note: When using multiple tags, separate each tag using a ‘/’ (forward slash), or hyphen.
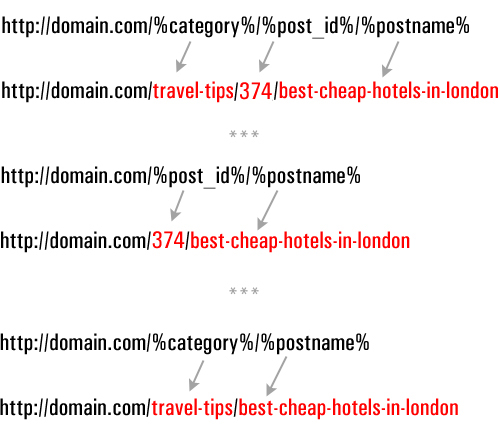
For a quick setup, choose the Custom Structure option, and enter the code below into the ‘Custom Structure’ field …
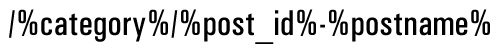
Or, use one of the following structures:
![]()
Tip: If you want search engine friendly URLs for your posts, but don’t want to use a custom permalink structure using tags, then choose Common Settings > Post name instead …
Choosing ‘Post name’ is the same as adding the /%postname%/ tag in ‘Custom Structure’.
Permalinks – Optional Settings
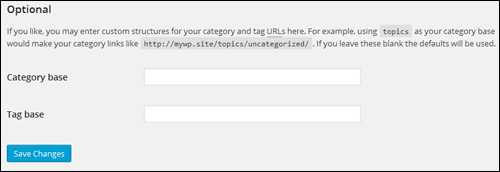
This section lets you configure custom structures for your category and tag pages.
This changes the ‘base’ category or tag for your URLs using the following syntax:
- domain.com/category_base/category_name
- domain.com/tag_base/tag_name
For example, using “recipes” as your category base would make your category links display as ‘http://domain.com/recipes/category_name/’.
So, if you make the following change in your permalinks Optional > Category base settings field …
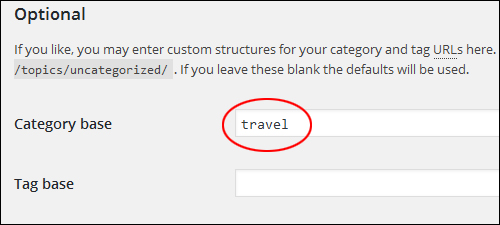
Your ‘category archives’ page URL will go from looking like this …
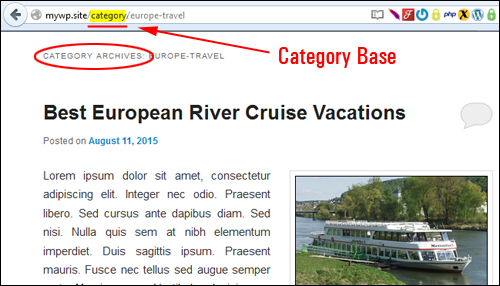
To this …
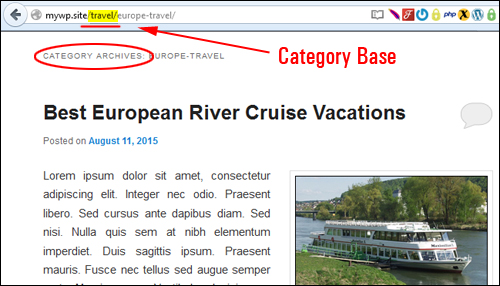
If you leave the optional settings fields blank WordPress uses the defaults.
Remember to save your changes when finished …
Permalinks – Useful Tips
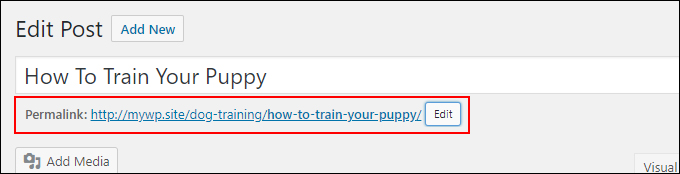
Sometimes, when you are creating a new post and haven’t given the content a post title yet, the WordPress Autosave feature will save your draft with an assigned numerical permalink (see the example URL in the screenshot below) …
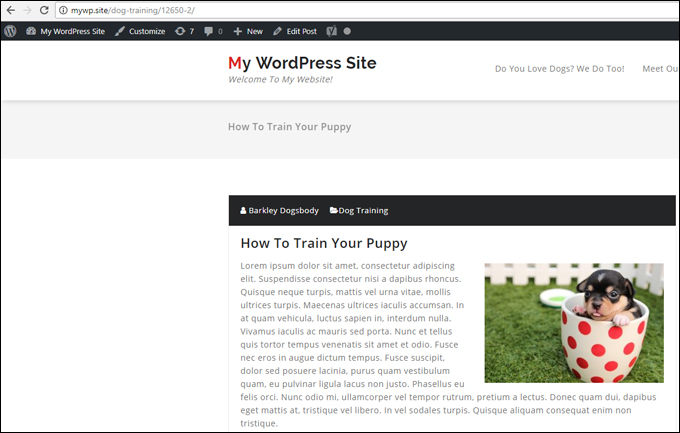
To fix this and give the post its proper permalink, go to ‘Edit Post’ …
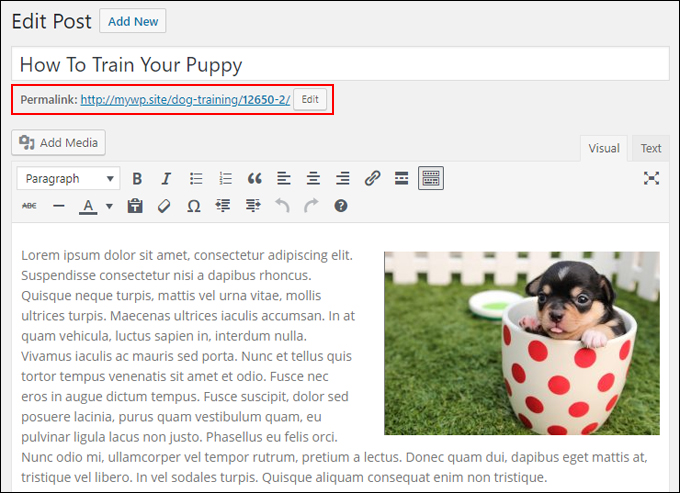
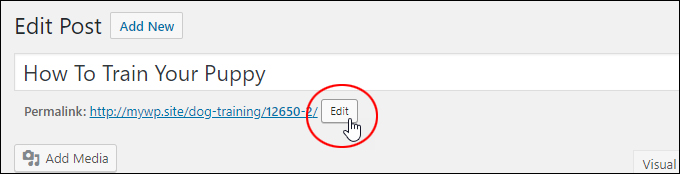
Click on the ‘Edit’ button in the post slug section …
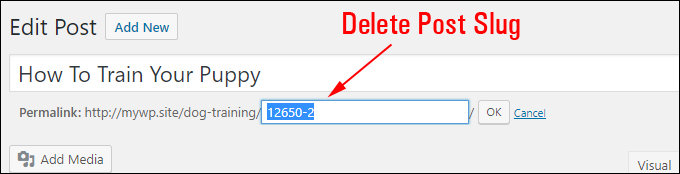
Select all content in the post slug field and delete it …
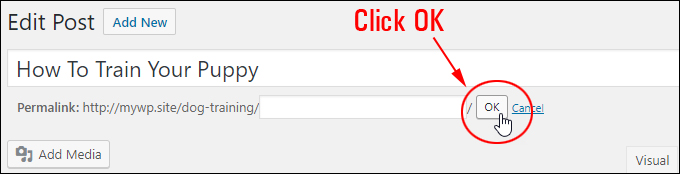
Click ‘OK’ …
The post slug entry will be replaced with the correct permalink based on your post title …
Here is a quick recap of the process …
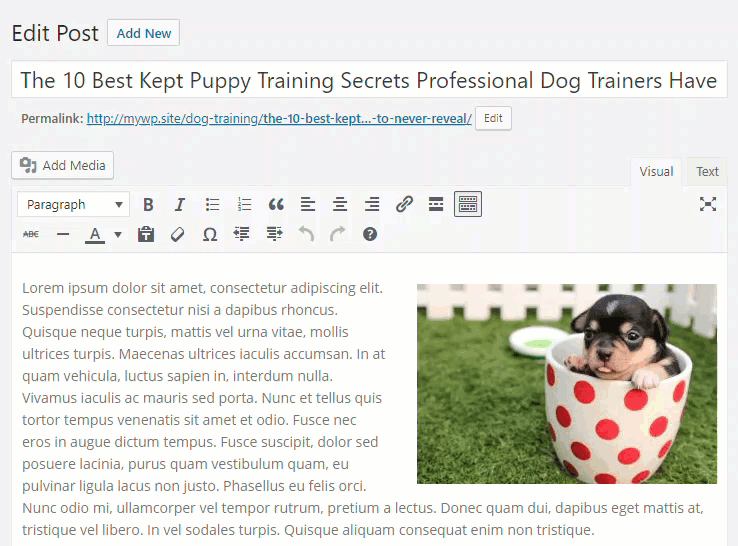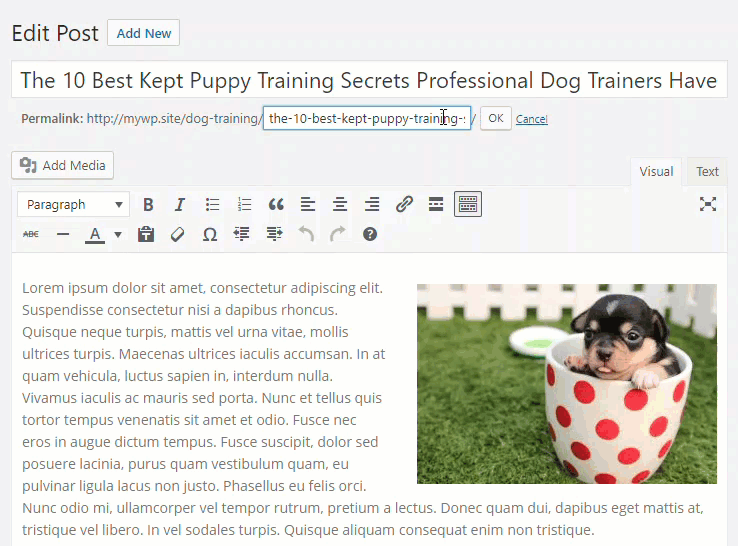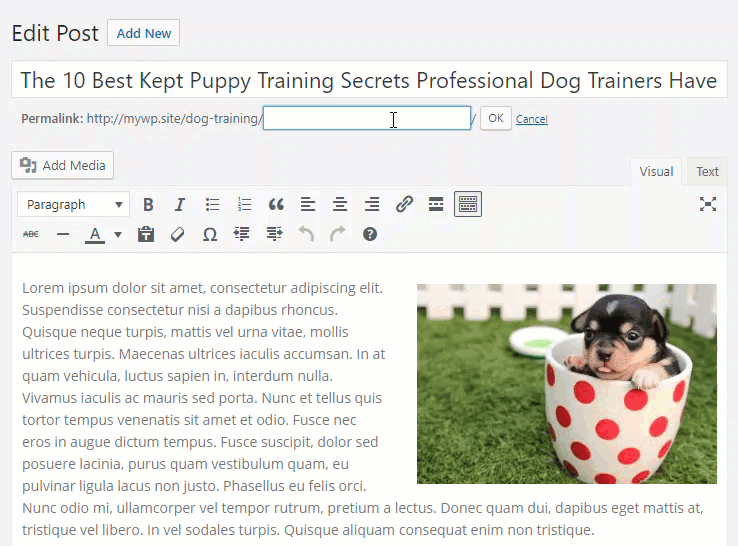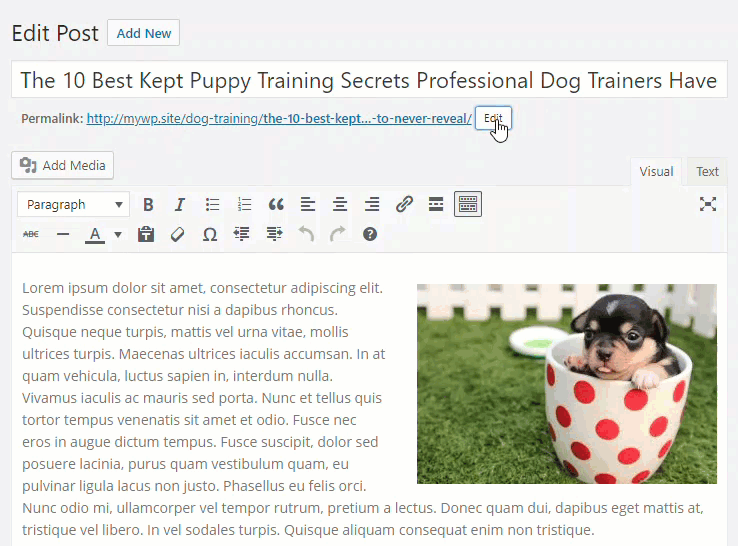
Remember to update your post to save the changes …
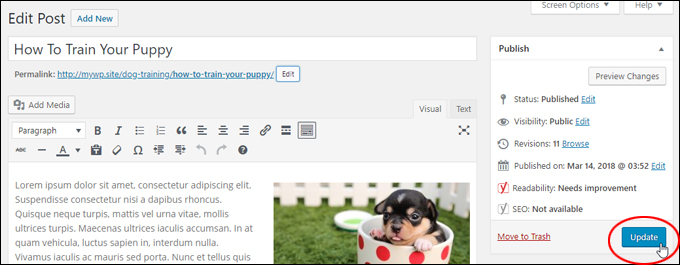
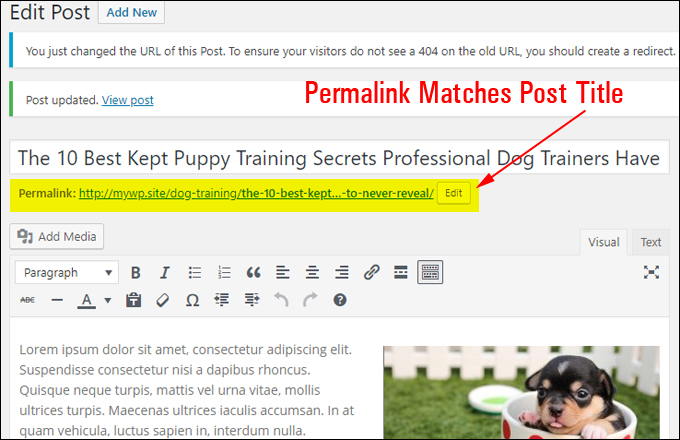
Your permalink should now reflect the new post title …
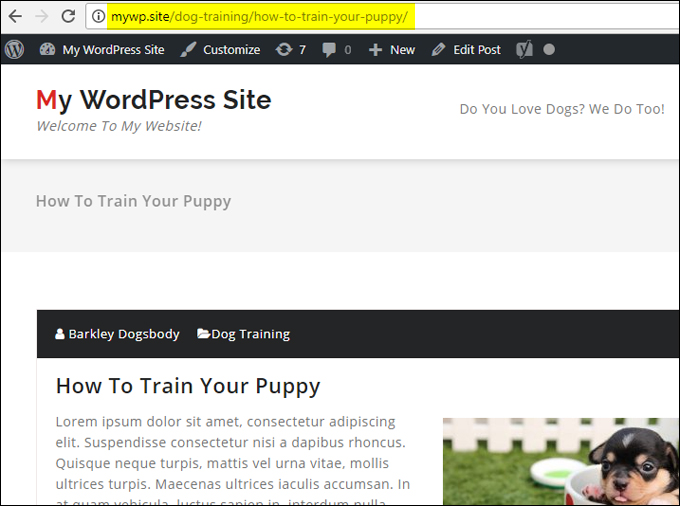
Note also that when you change the URL of a published post, you should also create a redirect link …
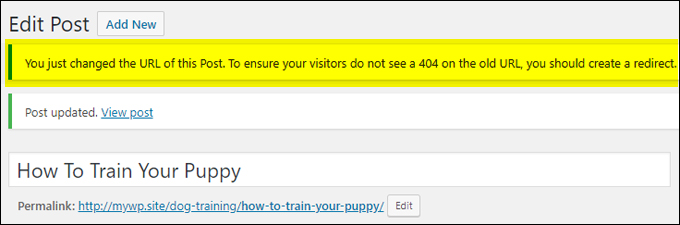
If you change your post title at a later date (e.g. you think of a more compelling post title or use a headline generator tool to help you come up with some killer post titles), remember to fix the permalink to match the new post title and add a redirection to the new post URL …
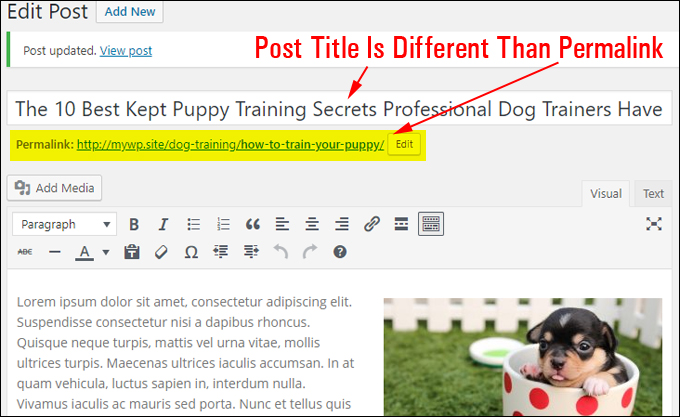
Make sure that your permalinks match the titles of your posts and pages to help site visitors find what they are looking for and ensure that search engines will better index your content …
Permalinks – Tips
Set Up Categories
To get the best benefit from using Permalinks, you will need to set up your WordPress Categories correctly. If you do not have any categories set up, adding a category tag to your permalink forces WordPress to use the default category (uncategorized).
According to WordPress SEO plugin developer Joost de Valk, here are some things to consider if you are wondering whether or not to add categories to your permalinks:
- If your domain is short and your category slug is short and descriptive (e.g. adds a relevant keyword or keyword phrase to your URL), you may want to use the category tag in your permalink.
- If your post slug (the part of your URL that identifies your post) is too long, it can make your post URL harder to share or copy and decrease the SEO benefit.
- Do you plan to post content under only one category or multiple categories? If you plan to post content under multiple categories, then we recommend not using the category tag in your permalink structure.
Despite being the subject of intense debate in WordPress SEO circles, when it comes to category vs no category there is no ”better” permalink structure to use. Choose a permalink structure that you think will suit your needs best. Your post URLs should be short enough to be attractive and long enough to be descriptive.
We provide detailed information about WordPress categories in other tutorials.
Avoid Time-Specific Permalinks
Another tip from Joost de Valk is that unless your website provides news, or there is a special reason why you need to create dated website URLs, it’s best to avoid choosing date-based permalink settings when setting up your site’s URLs.
(Avoid using URL structures that time-stamp your content)
Visitors are less likely to click on posts that are several years old, even if the content is relevant to the answers they are searching for.
What About Established Blogs?
Normally, your permalinks should be set up when you first install WordPress. This should be part of your website planning process.
![]()
If your website is already established or your site already has many posts indexed in the search engines and you would like to change the permalink structure, make sure that this is absolutely something that needs to be done, as changing permalinks after your site has already been running for a while could create issues and errors.
Add 301 Redirects
As you’ve seen in earlier screenshots, many WordPress site owners (or their web developers) are unaware of the SEO-friendly URLs feature of WordPress.
Maybe you started out using the default WordPress URL structure and now you want to optimize your site better for search engines. Perhaps your site was configured to display post dates in your URLs and now all of your posts are perceived as being out-of-date and you want to delete the date portion of your URLs.
The best way to modify your permalinks without affecting your site’s SEO in a negative way is to add ‘301 redirects’ to point links set up using the old permalinks syntax to web addresses that use the new syntax.
Search engines interpret a code ‘301’ as a link that has permanently relocated to another destination. 301 redirection is the most efficient and search engine friendly way to redirect users to new web page destinations and avoid ‘404’ (Page not found) errors if clicking on an old link.
To create an effective permalink syntax change and avoid damaging your rankings, sending visitors to broken links, etc. you will need to add your redirection system before changing the permalink structure of your site.
You can site using a WP redirection plugin like Simple 301 Redirects, or Redirection, or use the services of a professional to assist you with setting up and redirecting your permalinks correctly to avoid problems and troubleshoot any errors.
(Set up 301 redirects using plugins or use the services of a professional)
Congratulations! Now you know about the built-in system WordPress uses to display SEO-friendly URLs for your posts. To learn more about using Permalinks, refer to the WordPress codex here:
http://codex.wordpress.org/Using_Permalinks
***
"Learning WordPress has been a huge stumbling block for me. I've been looking for something that covers absolutely everything but doesn't cost an arm and a leg. Thank you so much ... you have just provided me with what I have been looking for! Truly appreciated!" - Tanya